In the year 2021, cryptocurrencies reached the zenith of their popularity. Cryptocurrency advertisements even found their way onto the screens during the Super Bowl, and many individuals fervently poured their investments into this novel form of currency. However, today, the enthusiasm has notably decreased, with infrequent references to Bitcoin and other digital currencies in ordinary news.
A short while ago, we witnessed Bitcoin’s precipitous drop by 70% after its vertiginous ascent. Following suit, other currencies, such as Ethereum and Dogecoin, followed a similar trajectory of decline. Cryptocurrencies have demonstrated susceptibility to fluctuations in interest rates, rendering crypto investors as susceptible as those who invest in traditional stocks.
Nonetheless, cryptocurrency is far from fading into obscurity in our lives. Numerous countries are embracing the concept of official cryptocurrency payments within their borders.
To gain a nuanced perspective on this issue, let’s embark on a journey through the evolutionary history of cryptocurrency, explore its endorsement by sovereign nations, and contemplate the imminent prospects for the forthcoming decade.
Concise History of Cryptocurrencies
The term “cryptocurrency” emerged in tandem with the introduction of the “Bitcoin” payment system. The Bitcoin protocol, conceptualized in 2008, was attributed to an individual or a group under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Under the same pseudonym, an article titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” was released on October 31, detailing how to utilize a peer-to-peer network to establish a trustless electronic transaction system. Subsequently, in 2009, the first open-source Bitcoin client was made available on SourceForge.
The inaugural recipient of a Bitcoin transaction was the programmer Hal Finney on January 12, 2009. In return for downloading the software, he received 10 Bitcoins from Satoshi Nakamoto. It’s estimated that Satoshi himself mined 1,000,000 Bitcoins in the early stages of their existence, following which he withdrew from the online realm, handing over the development responsibilities to Gavin Andresen.
The maiden instance of a retail purchase using Bitcoins transpired on May 22, 2010. On this day, an unidentified buyer acquired two pizzas from a pizzeria in Florida, paying with 10,000 Bitcoins.
On August 6, 2010, hackers uncovered a substantial vulnerability within the Bitcoin protocol. This vulnerability allowed transaction authors to create an arbitrary number of coins. As a result, on August 15, a singular transaction expended 0.5 Bitcoins to dispatch a staggering 92 billion Bitcoins to two distinct addresses within the network. The error was swiftly detected and rectified by experts, leaving the cryptocurrency devoid of any noteworthy security deficiencies.
In the wake of Bitcoin’s triumph, a slew of alternative currencies, known as altcoins, sprouted globally from 2011 onward, hinging on the same foundational code. Notable among these alternatives are Ethereum and Litecoin.
May 2011 witnessed the introduction of the inaugural Bitcoin payment processor, BitPay. This innovation empowered businesses to accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment. For example, the platform WikiLeaks embraced cryptocurrency donations.
As a result, the Bitcoin transaction ledger, often known as the blockchain, came into existence. Among the pioneers of cryptocurrency acceptance were OkCupid, Foodler, Zynga, Newegg, Bidorbuy, Dell, and WordPress. Even Steam briefly embraced cryptocurrency, though it renounced the endeavor in 2017 due to sluggish transaction speeds.
In October 2013, Robocoin and Bitcoiniacs unveiled the world’s first Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver, Canada.
Nonetheless, cryptocurrencies faced a substantial amount of criticism.
- On December 4, 2013, Alan Greenspan called Bitcoin a “bubble.”
- Warren Buffett echoed this sentiment on March 13, 2014, labeling Bitcoin a “mirage.”
- Subsequently, on January 25, 2018, Alan Soros voiced his opposition to Bitcoin, again categorizing the currency as a “bubble.”
To some degree, these experts’ assessments were held. Cryptocurrencies did tend to decline after experiencing significant surges.
As previously discussed, cryptocurrency’s popularity waned following its distinctive boom in 2021. However, the pattern of growth and subsequent decline in cryptocurrencies is explicable. Let's discuss the most famous surges and plunges of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Rises and crashes of Cryptocurrency Bubbles
The rapid rise and sudden fall of cryptocurrency values are called the "cryptocurrency bubble.” Since 2009, there have been four market booms followed by four subsequent crashes in cryptocurrencies. Let’s delve into the underlying reasons for these recurring cycles.
2011: the first alarming bells
The inaugural occurrence of a “cryptocurrency bubble” in 2011 was modest and didn’t lead to catastrophic consequences. However, during this period, the adoption of cryptocurrencies among individuals and businesses was still in its nascent stage.
Bitcoin’s meteoric ascent occurred in February 2011, propelling its price to $0.16. Subsequently, a substantial “crash” followed in April, causing the currency’s value to retract to $0.67. This minor surge was spurred by discussions on the Slashdot website, focusing on the emerging cryptocurrency market.

Nevertheless, Bitcoin underwent another noteworthy surge in June 2011, reaching a price pinnacle of $29.58. This remarkable growth can be attributed to an article published by Gawker, which shed light on the Silk Road online marketplace. However, the triumphant phase of Bitcoin proved to be short-lived, as its price experienced a steep descent to $2.14 in November of the same year.
2013-2015: a curvy road to the top
A significant surge in Bitcoin’s valuation unfolded throughout 2013. By November, its price had soared to a remarkable $1,127, only to experience a subsequent plummet to $172.15 in January 2015.
2017-2018: new challenges - new players
The year 2018 bore witness to the monumental event known as the Great Cryptocurrency Crash, during which numerous voices prophesied the downfall of Bitcoin. This upheaval, as projected, ensued on the heels of an unprecedented boom in 2017.
On December 17, 2017, Bitcoin reached its zenith price of an astonishing $19,783. Nonetheless, within a mere five days, by December 22, it had tumbled by 45%, settling below the $11,000 mark. Yet the challenges for crypto investors didn’t end there.
By September 2018, cryptocurrencies had dwindled by a staggering 80% from their zenith in January. November of the same year saw Bitcoin’s market capitalization dip beneath the $100 billion threshold, and come December, its value had plummeted further to $3,100.
This downturn stemmed from several contributing factors:
- Speculation surrounding the potential ban of cryptocurrency trading in South Korea.
- A massive hack targeting a prominent Japanese cryptocurrency exchange resulted in a pilferage of $530 million, leading to an indefinite suspension of trading.
- Twitter, Google, and Facebook implemented a ban on token advertisements and sales.
The anticipation of a “bubble” burst had already been voiced by Weird magazine back in 2017, at the height of the currency’s exponential growth. Among the beneficiaries of the cryptocurrency upsurge, Binance emerged as the preeminent victor, establishing itself as the largest platform for cryptocurrency trading.
2020-2022: crossing the line of global cocern
While previous cryptocurrency bubbles might have gone unnoticed by the general populace, the bubble of 2020-2021 became a globally recognized phenomenon.
In November 2020, Bitcoin broke its record as its price surged beyond $19,000. On January 3, 2021, another astonishing spike occurred, propelling the currency’s value by 17% in a single day, reaching $34,792. By January 8, 2021, the price had catapulted to $50,000; by February 16, 2021, it had reached an extraordinary peak of $66,794.
However, as early as January 11, the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority warned crypto investors, alerting them to be prepared for the potential loss of their entire investment.
Other cryptocurrencies followed Bitcoin’s trajectory, riding the waves of its success. For instance, initially conceived as a joke, Dogecoin experienced a staggering 20,000% increase in value compared to the previous year.
A subsequent cryptocurrency crash unfolded in May 2021, leading to nearly all coins experiencing double-digit percentage losses. On May 19, Bitcoin plummeted by 30%, Ethereum by 40%, and Dogecoin by 45%.
Around the same time, Tesla declared the suspension of cryptocurrency-related transactions, and China’s central bank reaffirmed its stance against using digital currencies for financial transactions.
Nevertheless, by July 19, cryptocurrencies had embarked on another period of growth. Bitcoin achieved the $52,533 milestone again, while Ethereum surged by over 100% to reach $3,952. Both currencies continued their ascent until November 19, when they reached their zenith. Bitcoin soared to $67,599, and Ethereum reached an impressive $4,812.
A substantial downturn in the cryptocurrency market commenced in late 2021, with Bitcoin experiencing a 30% plunge and Ethereum a 23% drop.
By December 2022, The Washington Post declared that the crypto bubble had burst. Cryptocurrencies continued to depreciate, and by mid-2023, the value of Bitcoin had descended to $26,000.
The recurring cycles of booms and crashes in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies substantially hinder the widespread adoption of this technology worldwide. Nevertheless, numerous countries are willing to integrate cryptocurrencies as official payment systems. Let’s delve into this topic.
Making things official: the governments experimenting with cryptocurrencies
What prompts governments to embrace cryptocurrencies? There are several underlying reasons for this phenomenon.
First and foremost, some countries grappling with hyperinflation in their traditional currencies are increasingly turning to cryptocurrencies, primarily due to restricted access to foreign currencies. Adopting digital currency offers a more viable alternative in countries like Venezuela, Vietnam, Nigeria, and Kenya, where foreign investors are in short supply. Notably, these countries exhibit significant peer-to-peer (P2P) transaction volumes. For the residents of these regions, cryptocurrencies provide a means to safeguard their earnings and elevate their quality of life in response to the persistent threat of currency devaluation.
Secondly, countries are incorporating cryptocurrencies as part of their strategy to decentralize foreign central bank policies. This strategic move allows a nation to globalize its economy and enhance its appeal to foreign investors, diversifying its economic landscape.

The first country to formally adopt cryptocurrencies was El Salvador. Within this nation, both the US dollar and Bitcoin are accepted as valid transaction modes. This progressive governmental stance has not only streamlined import and export processes for Salvadoran merchants but has also facilitated real estate transactions by foreign investors, who can now comfortably use digital currency for their purchases.
There are two main ways to bring cryptocurrencies into use:
- Adoption of Existing Cryptocurrencies
- Digitization of Conventional Currency
This strategy involves the widespread incorporation of an already existing cryptocurrency. El Salvador, for instance, has embarked on this path by collaborating with the Strike company to establish the requisite infrastructure for Bitcoin transactions. A critical aspect of successful cryptocurrency integration is ensuring the economy’s autonomy from governmental interventions. This independence empowers merchants to engage in unhindered international trade and safeguards against potential censorship.
When a country’s central bank harbors reservations about externally governed currencies, it may create a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). The nation’s central bank directly issues such a currency. The United States, for instance, has chosen this course of action with the dollar. As a result, possessing 50 digital dollars now holds the same value as keeping the same amount in physical currency. CBDC is lauded for its enhanced security and stability. However, these digital currencies function like their traditional counterparts, subject to state policies and global events. Moreover, integrating CBDC doesn’t necessitate blockchain technology, which distinguishes it from other cryptocurrencies.
According to a survey by YouGov, 38% of Americans believe cryptocurrency will be widely used for legal transactions within the next 10 years. In the case of Latin America, a global survey by Statista has shown that Argentina leads in this region, with 21% of its residents owning digital currency.
However, the mass adoption of cryptocurrencies isn’t a universal trend. In certain countries, such as China, cryptocurrency is completely banned. Moreover, there is currently little chance that cryptocurrencies will fully replace traditional currencies. The question is, why?
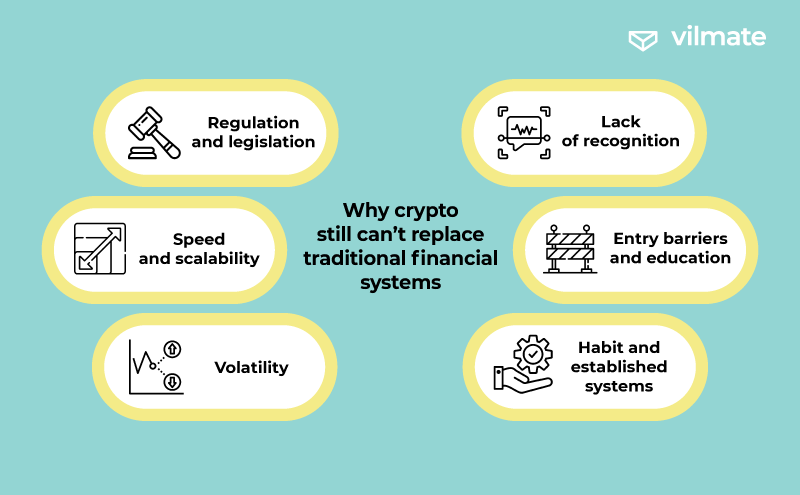
Why crypto still can’t replace traditional financial systems
Replacing traditional financial systems with cryptocurrencies is a complex and multifaceted process that encounters various challenges and limitations. Here are several reasons why cryptocurrency won't entirely replace traditional financial methods.
- Regulation and legislation: Cryptocurrencies face diverse regulatory challenges across different countries. The absence of clear and consistent rules and laws can lead to uncertainty and risks for users and investors. Some countries restrict or prohibit the use of cryptocurrencies, limiting their adoption.
- Speed and scalability: Some cryptocurrency networks encounter limitations in transaction speed and scalability. This problem can result in delays and high fees for transfers, making them less convenient for everyday financial operations.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are often subject to significant fluctuations. This factor poses risks for investors and makes cryptocurrencies less stable as stores of value and means of exchange compared to traditional currencies.
- Lack of recognition: Despite growing popularity and recognition by some institutional investors, cryptocurrencies haven’t been fully acknowledged as a legitimate means of exchange in many economic spheres. The lack of support from governments and central financial organizations restricts their usage.
- Entry barriers and education: Utilizing cryptocurrencies requires technical literacy and an understanding of blockchain technology. It can be a barrier for many individuals, especially the older generation or those without access to technical resources.
- Habit and established systems: Traditional financial methods have existed for decades and are deeply integrated into people’s everyday lives. The habit of using bank accounts, credit cards, and other traditional financial instruments is entrenched, and changing this lifestyle takes time and effort.
Overall, cryptocurrencies hold great potential, but overcoming numerous technical, regulatory, social, and practical challenges is essential to replace traditional financial systems successfully.
Future perspectives for the nearest decade
The future of cryptocurrencies remains uncertain, defying any definitive predictions. Those experts making such categorical forecasts are unlikely to divulge such valuable insights to the public.
In contrast to stocks and bonds, which find their foundation in commitments to forthcoming revenue streams, cryptocurrencies lack such backing and rely heavily on investors’ trust.
Several central banking figures have labeled cryptocurrencies as fraudulent. For instance, the President of the European Central Bank has proclaimed that cryptocurrencies lack intrinsic value and are essentially baseless. However, paradoxically, the European Central Bank is simultaneously proposing its own digital currencies, which aren’t reliant on blockchain technology.
Policymakers and central banks have three viable courses of action.
- To disregard cryptocurrencies altogether. It’s a seemingly uncomplicated response, given that cryptocurrencies are unlikely to supplant traditional currencies in the foreseeable future.
- To institute a ban on cryptocurrencies. Certain heads of state express concern that substantial cryptocurrency transactions could disrupt the stability of their national currencies. However, any potential ban would require global consensus to be genuinely effective.
- To establish regulations for cryptocurrencies. Regulation is considered the most prudent approach and merits the primary focus of governmental efforts.
In all likelihood, over the ensuing decades, governments will opt for the regulatory route concerning cryptocurrencies. Expectations include witnessing several more cycles of value surges and declines. Perhaps most crucially, the persistence of cryptocurrencies is undeniable; they’re here to stay.
Exploring Cryptocurrency Opportunities for Businesses
The widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology presents various business opportunities and challenges. Below are several strategic steps that companies can contemplate to harness the potential of this evolving trend.
- Integration of cryptocurrency payments: Consider the feasibility of incorporating cryptocurrency as a payment method. Such a move has the potential to broaden your customer base.
- Development of proprietary technological solutions: Delve into how blockchain technology could streamline your business operations. Crafting your decentralized applications or leveraging the capabilities of smart contracts can notably enhance operational efficacy.
- Leveraging technology for transparency and verification: The blockchain’s capabilities can be harnessed to establish a robust framework for enhancing transparency and verifying the authenticity of products. This aspect becomes particularly significant in supply chain tracking and verifying product provenance.
- Creating loyalty and rewards ecosystems: Crafting bespoke tokens or cryptocurrencies for loyalty programs can incentivize customer engagement and catalyze purchasing behavior.
Recognizing the individuality of each business, the manner in which cryptocurrencies are adopted will inherently hinge on its distinctive attributes and overarching goals. A meticulous exploration of the technology and a comprehensive assessment of potential benefits and pitfalls are essential precursors to informed decision-making.
If you require assistance with cryptocurrency integration or blockchain implementation in your business, feel free to contact Vilmate. We possess the expertise to assist in turning all your ideas into reality. We can establish a team for projects of any complexity from scratch, or augment the existing infrastructure with our professionals.
Stay tuned with Vilmate! The progress will never stop, and the topics for discussion will never dry out :)




